Quick Reference
Is It OK to Take Too Much Vitamin B12 Supplement?
Although vitamin B12 is generally considered safe, high doses may worsen kidney function in people with diabetes or increase cancer risk. Pregnant women should avoid taking large dosages of B12 supplements unless under a healthcare professional's care.
Who Needs Vitamin B12 Supplements?
- People who are over the age of 50
- People who follow vegetarian or vegan diets
- People with digestive disorders
- People who have had weight-loss surgery or other stomach or intestinal surgery
Why Is Vitamin B12 Important?
Vitamin B12 is vital for many body functions. It helps to:
- Make DNA
- Build red blood cells
- Keep nerves healthy
What Happens If Your B12 Is Too High?
- Acne Outbreaks
- Several Side Effects on Diabetic Nephropathy Patients
- Increases Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Increases the Risk of Cancer
- Increases Lung Cancer Risk in Men
- Increases the Risk of Hip Fracture in Postmenopausal Women
Vitamin B 12 is an essential vitamin that our bodies need for many important functions. It helps to make DNA, red blood cells, and nerves. Animal products like meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy contain Vitamin B12.
Most people get enough vitamin B 12 from their diet. But, some people may not get enough vitamin B 12 because they have trouble absorbing it from food. They may need to take vitamin B 12 supplements.
The body does not store vitamin B 12, so it is important to get enough of this essential nutrient every day. But is It OK to take too much vitamin B12 supplement? Let's discuss this topic further.
Why is vitamin B12 important?
Vitamin B12 is vital for many functions in the body, according to NIH. [1] It helps to:
- Make DNA
- Build red blood cells
- Keep nerves healthy
Vitamin B12 is super important for your body. A deficiency in B12 can lead to an array of health issues, including neurological symptoms, which underscores the importance of having adequate levels of this vitamin.
If you don't get enough B12, you could feel tired, have trouble balancing, or your nerves could hurt. So, it's a good idea to make sure you're getting enough B12 to stay healthy and feel good! But, only a small percentage of people are actually deficient in vitamin B12.
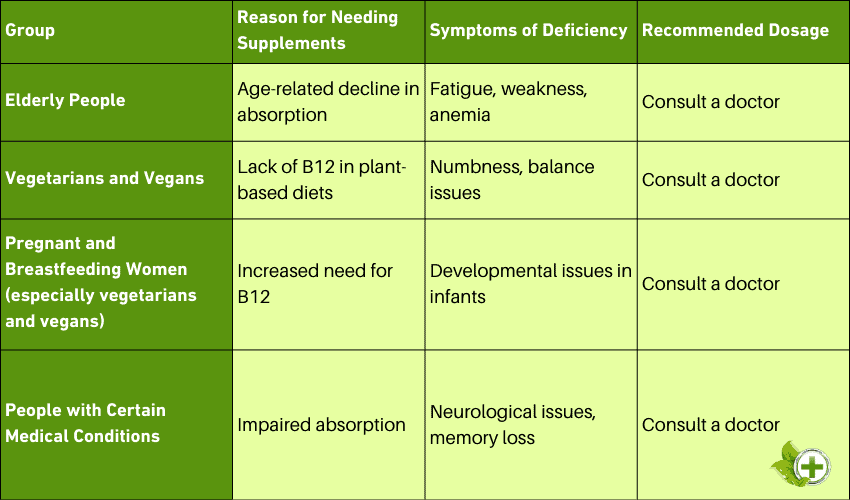
Who needs vitamin B12 supplements?
A study from MedlinePlus tells us that some people might not have enough Vitamin B12 in their bodies. [2] Here are four types of people who need to pay extra attention to getting enough of this vitamin:
- People who are over the age of 50
As people get older, their bodies sometimes have a harder time getting Vitamin B12 from the food they eat. This is because as you age, your stomach doesn't make as much acid, and you need that acid to help absorb the vitamin. So, older people might need to take extra Vitamin B12 to make sure they have enough in their bodies to stay healthy. [3]
- People who follow vegetarian or vegan diets
Vitamin B12 is often found in animal products like meat and eggs. So, people who are vegetarians or vegans might not get enough of this vitamin because they don't eat those kinds of foods. They need to find other ways to get Vitamin B12 to stay healthy.
- People with digestive disorders
Some people have illnesses that make their stomachs and intestines not work as well. These illnesses include Crohn's disease, celiac disease, and pernicious anemia.
Because of this, they might have a hard time getting enough Vitamin B12 from the food they eat. This vitamin is important to help them stay strong and healthy.
- People who have had weight-loss surgery or other stomach or intestinal surgery
Some people get surgery to help them lose weight or to fix problems in their stomach and intestines. After the surgery, their bodies might have a hard time getting Vitamin B12 from food. They need this vitamin to help heal and stay healthy.
If any of the following categories applies to you, you may need a vitamin B12 supplement.

How much B12 can you safely take a day?
Everyday, people need a certain amount of Vitamin B12 to stay healthy. For teens and adults over 14, they should get 2.4 mcg (that's a super tiny amount) of Vitamin B12 each day. But not everyone needs the same amount!
Moms-to-be and moms who are breastfeeding need a bit more. If a mom is expecting a baby, she should try to get 2.6 mcg of Vitamin B12 every day. If she's breastfeeding, she needs 2.8 mcg daily. This helps both mom and baby stay strong and healthy. [4]
Whether you're getting your Vitamin B12 from food or a vitamin pill, the amount you need is the same. But remember, there's a limit! You shouldn't have more than 2,000 mcg of Vitamin B12 from vitamin pills each day. This is what the experts say is a safe amount to take. [5]
Balancing Your Vitamin B12 Intake
When considering the intake of Vitamin B12 or any supplement, it’s crucial to embrace a balanced approach. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods can be a natural way to maintain optimal health.
Natural Sources of Vitamin B12
- Seafood, particularly scallops
- Meat and poultry
- Eggs
- Dairy products
For those exploring plant-based diets or seeking alternative supplement options, flavonoid supplements can be a valuable resource.

Is it ok to take too much vitamin B12 supplements?
Vitamin B12 is a special kind of vitamin that dissolves in water. This means your body doesn't keep it stored up, so you need to make sure you get enough of it every day.
Here's a cool fact: there are two main types of vitamins. One type, called water-soluble vitamins, dissolves in water and goes quickly into your blood. Your body takes what it needs and gets rid of the rest when you go to the bathroom. Vitamin B12 and vitamin C are like this. The other type is fat-soluble vitamins. Your body's liver and fat store these vitamins. Vitamins A, D, E, and K are in this group.
Now, back to Vitamin B12. The experts at Harvard School of Public Health say there's no maximum amount that you can take because it doesn't usually cause any problems. But, it's still not a good idea to take way too much (like more than ten times the normal amount you need each day) because it could make you feel not so great. [6]

What happens if your B12 is too high?
Megadoses of Vitamin B12 can have adverse health effects, as too much of any nutrient can be harmful. The following are some of the possible health concerns of taking too much vitamin B12 supplement:
Acne outbreaks
Some research has found that taking a lot of Vitamin B12 can lead to acne, which means getting pimples on your skin. [7] There were a few studies, and one of them is in a big library of medical reports, that showed people getting acne after getting Vitamin B12 shots.
But here's something important - these studies were about people who got Vitamin B12 through shots, not the kind you eat or take as a pill. So, if you're eating foods with Vitamin B12 or taking vitamin pills, it might not be the same. [8] [9] [10]
Several side effects on diabetic nephropathy patients
There was a study called "Effect Of B-Vitamin Therapy" that the NIH (a big health organization) talked about. It found something important for people with a type of kidney problem called diabetic nephropathy. When these people took big amounts of B vitamins, including Vitamin B12, their kidneys didn't work as well and got worse faster. [9]
In another study, they found out that taking extra B vitamins could actually be risky for these people. It could increase the chances of serious health problems like heart attacks, strokes, and even dying. So, it's super important for people with this kidney issue to be careful with taking extra B vitamins. [10]
Increases risk of autism spectrum disorder
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a condition that makes communicating and socializing challenging for some kids. The CDC says that about 1 in 68 kids in the U.S. have ASD. Different things, like genes and stuff in the environment, can cause it. [11]
Vitamin B12 is super important for our brains and nerves. But, some people are starting to wonder if it might have something to do with ASD.
There was a study in a big medical library that said too much Vitamin B12 might increase the chance of a baby being born with ASD. Moms who took a lot of Vitamin B12 when they were pregnant had kids who were more likely to have ASD than moms who didn’t take as much. [12]
But don’t get too worried yet. We need more studies to be sure about this. For now, it’s a good idea for pregnant moms to not take a lot of Vitamin B12 unless their doctor says it’s okay.
Increases the risk of cancer
Some studies, called thin cohort studies, help scientists figure out what might increase the risk of getting certain diseases. But these studies aren't as strong as others, like randomized controlled trials, in proving those risks. In a thin cohort study, scientists look at one group of people and compare how often a disease happens in that group to another group. It helps spot possible risk factors for diseases, but it can't prove that those factors actually cause the disease.
There was a study called "Elevated Vitamin B12 Levels and Cancer Risk" that used this method. It found that people with higher levels of Vitamin B12 might have a higher chance of getting certain types of cancer, like liver and pancreas cancer. But remember, this study can't prove that having extra Vitamin B12 actually causes cancer. We need more research to know for sure. [13]
Also, this study looked at people with high levels of Vitamin B12 in their blood, but it didn't say if this was because they took extra B12 supplements or not. So, it's hard to make clear conclusions from this study alone.
Increases lung cancer risk in men
Studies have shown that men who take a lot of vitamin B6 and B12 as individual supplements might have a higher chance of getting lung cancer. The risk is about 30-40% higher. But this wasn’t true for women or for people who got these vitamins from multivitamins (those are the pills that have lots of different vitamins in them). [14]
Men who took a lot of vitamin B6 or B12 for a long time had almost double the chance of getting lung cancer, especially if they smoked.
But here’s something different - the study also looked at another vitamin, folic acid, and didn’t find any link between it and lung cancer.
So, the main takeaway is that taking a lot of vitamin B6 and B12 supplements might make men more likely to get lung cancer. This is especially important for guys who smoke to know about.
Increases the risk of hip fracture in postmenopausal women
There was a study that looked at older women who had gone through menopause to see if taking a lot of vitamins B6 and B12 affected their bones. The study found that women who took a lot of these vitamins were more likely to break their hips. [15]
The risk was even higher for women who took a lot of both vitamins B6 and B12 - they had almost a 50% higher chance of breaking their hip compared to women who didn't take as much of these vitamins.
So, this study tells us that we should be careful with taking vitamin supplements, especially in large amounts, because they can sometimes have negative effects on our health.
Bottom line
While the risk of overdosing on Vitamin B12 is low, moderation is key. Balancing your intake, being mindful of your body’s signals, and seeking professional advice can ensure that you’re nurturing your body in the most effective ways. After all, in the journey of health and wellness, balance is not just a goal but a pathway to a vibrant, energetic life, free from the worries of diseases, including those that can be transmitted by pets.
In the quest for optimal health, exploring natural and holistic paths, while being informed about the potential risks and benefits of supplements, can pave the way for a life of vitality, wellness, and balance.
FAQ
What Are The Long-Term Effects Of Taking Too Much Vitamin B12?
The long-term effects of taking too much vitamin B12 can depend on the dosage. At high levels, it can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It can also interact with other medications you're taking and cause serious side effects. Therefore, it's always essential to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, including vitamin B12.
Who Should Not Take A Vitamin B12 Supplement?
People who should not take a vitamin B12 supplement are those who get enough vitamin B12 in their diets. This includes:
people who eat meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products;
people who eat fortified breakfast cereal; and
people who use a multivitamin that contains vitamin B12
References
- NIH: Vitamin B12
- MedlinePlus: Vitamin B12
- Pubmed: Effects of aging and gastritis on gastric acid and pepsin secretion in humans
- MedlinePlus: Vitamin B12
- Pubmed: Oral vitamin B12 versus intramuscular vitamin B12 for vitamin B12 deficiency
- The President and Fellows of Harvard College: Vitamin B12
- National Library of Medicine: Vitamin B12-induced acneiform eruption
- Pubmed: Acneiform eruption in a 5-year-old due to vitamin B12 supplementation
- Pubmed: Acneiform eruption due to vitamin B12: a problem still unsolved
- Pubmed: Acneiform eruptions caused by vitamin B12: A report of five cases and review of the literature
- NIH: Effect of B-vitamin therapy on progression of diabetic nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial
- Pubmed:Effect of B-vitamin therapy on progression of diabetic nephropathy
- National Library of Medicine: Maternal Multivitamin Intake, Plasma Folate and Vitamin B12 Levels and Autism Spectrum Disorder Risk in Offspring
- PubMed Journal: Elevated Vitamin B12 Levels and Cancer Risk in UK Primary Care
- National Library of Medicine: Long-Term, Supplemental, One-Carbon Metabolism–Related Vitamin B
- JAMA Network: Association of High Intakes of Vitamins B6 and B12 From Food and Supplements With Risk of Hip Fracture Among Postmenopausal Women in the Nurses’ Health Study
⚠️Disclaimer: The information provided on this health blog is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.







